7. Repeating the Same Phrases
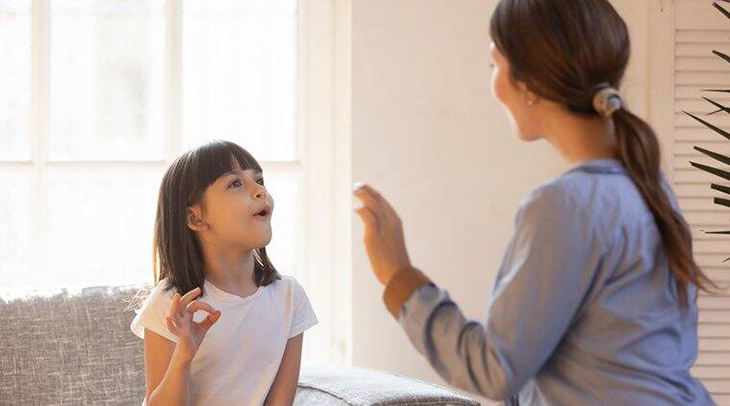

People who have echolalia repeat sounds and sentences they hear. They may be unable to communicate properly because they find it difficult to articulate their own ideas. Someone suffering from echolalia, for example, may only be able to repeat a question rather than answer it. Echolalia is frequently an attempt to communicate, study, or practice language. Echolalia is not the same as Tourette syndrome, in which a speaker may yell or say strange things as part of their tic. The speaker has no control over what they say or when they say it in this scenario. Repetitive speech is a common feature of language development, especially in young babies learning to communicate. Most children will begin to mix in their own utterances with repetitions of what they hear by the age of two. Most children’s echolalia will be minimal by the age of three. Echolalia is common in autistic children and children with developmental impairments, especially if they have delayed speech development. Identifying why and how your child uses echolalia will aid in the development of a therapy strategy. A language pathologist can be a helpful ally to consult. The basic symptom of echolalia is the recurrence of previously heard phrases and noises. It can be immediate, with the speaker immediately repeating something after hearing it. It can even be delayed, with the speaker repeating information that was heard hours or days before. Other symptoms of echolalia include conversational dissatisfaction, melancholy, and muteness. When asked questions, a person suffering from echolalia may become excessively agitated. When children learn a spoken language, they all suffer echolalia. Most mature into autonomous thinkers, but some continue to repeat what they hear. Children with communication disorders retain echoed expressions for considerably longer. Autistic children are more vulnerable to echolalia. Some people only have this problem when they are disturbed or anxious. Others are constantly subjected to it, which may eventually drive them to become mute since they are unable to express themselves. Adults suffering from acute amnesia or brain trauma may develop echolalia while they attempt to restore their ability to communicate.