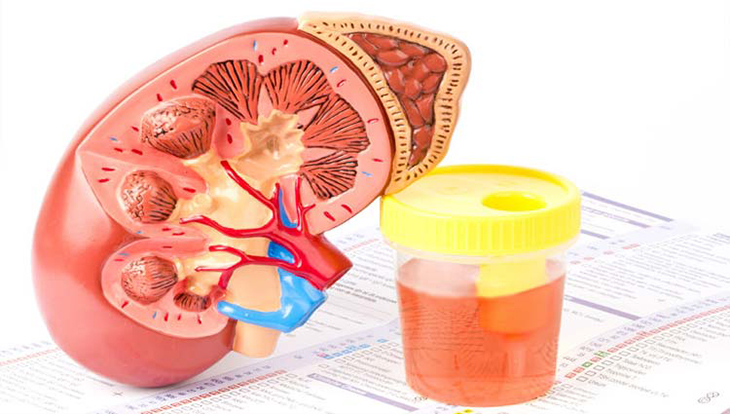
Blood in your urine can be concerning. While the reason is often innocuous, blood in the urine (hematuria) can signify a dangerous condition. The presence of blood in a person’s urine is known as hematuria. Gross hematuria occurs when a person can see blood in his or her urine, while microscopic hematuria occurs when a person cannot see blood in his or her urine but can see it under a microscope. The presence of red blood cells indicates gross hematuria, which results in pink, red, or cola-colored urine. Red pee requires very little blood, and the bleeding is frequently painless. However, passing blood clots in your urine might be painful. Bloody urine can develop without any other symptoms or indicators.
If you see blood in your urine, make an appointment with your doctor. Your urine may turn red if you take certain medications, such as the laxative Ex-lax, or eat specific foods, such as beets, rhubarb, or berries.
A change in urine color caused by medicines, food, or exercise may be temporary, but read on to find out more about what causes it.
1. Urinary Tract Infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) affects any component of your urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections affect the bladder and urethra in the lower urinary system. Women are more likely than men to have a urinary tract infection. A bladder infection can be both painful and unpleasant. If a UTI spreads to your kidneys, though, it might have significant implications. Antibiotics are commonly used to treat urinary tract infections. However, you may take precautions to avoid acquiring a UTI in the first place.
Bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and multiply in the bladder, resulting in urinary tract infections. Despite the fact that the urinary system is designed to keep such small invaders out, these defenses occasionally fail. Bacteria may take root and grow into a full-blown infection in the urinary tract if this happens. The bladder and urethra are the most prevalent sites for UTIs in women.