According to a new study, artificial intelligence (AI) can help detect early signs of cancer in chest X-rays.
Research shows that an AI tool can accurately differentiate between normal and abnormal chest X-rays in a clinical setting just as effectively as professional radiologists. This is especially significant because as one editorial paper shared, radiology departments are often understaffed.
Abnormal chest X-rays can be indicative of a number of different health conditions, including cancer and many chronic lung diseases. Scientists share that an AI tool that has the ability to accurately classify normal and abnormal X-rays would be of great help to reduce the already heavy workload of most radiologists.
Study co-author and radiologist from the Herley and Gentofte Hospital in Copenhagen, Dr. Louis Lind Plesner, shared in a report from Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), “Artificial intelligence has shown great promise, but should always be thoroughly tested before any implementation.”
In the study, the researchers used a commercially available AI tool to analyze the chest X-rays of 1,529 patients from four different hospitals located in Denmark.
These chest X-rays were from different emergency department patients, in-hospital patients, and outpatients. For reference standards, two board-certified radiologists were used, while a third radiologist was used in cases of disagreements.
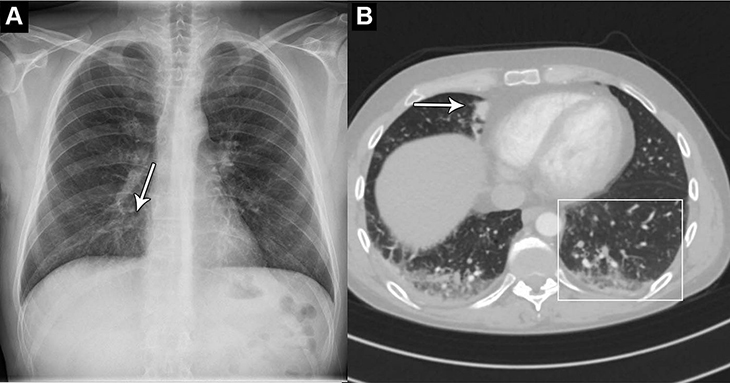
The AI tool correctly identified abnormal chest X-rays with a 99.1% sensitivity rate, including those with critical, remarkable, and unremarkable abnormalities. In 10 cases there were false negatives, of which 9 were clinically insignificant. As for the significant one, which was a subtle lesion, it was also missed by one of the attending radiologists.
Dr. Plesner explained, “The most surprising finding was just how sensitive this AI tool was for all kinds of chest disease. In fact, we could not find a single chest X-ray in our database where the algorithm made a major mistake.”
“Furthermore, the AI tool had a sensitivity overall better than the clinical board-certified radiologists,” he added.
Dr. Plesner also said that the AI tool managed to perform especially well at identifying normal X-rays at a rate of 11.6% for the outpatient group.
He also suggested that these findings, which were published in the journal Radiology, indicate that this AI model would perform well in outpatient settings with a high prevalence of normal chest X-rays.
The editorial on this topic praised the potential of the study’s key finding, which was the ability to handle 7.8% of all normal readings for radiologists. However, it also suggested that more research is needed to ensure that radiologists are not putting patients at risk for a mere 7.8% in workload reduction either.
Overall, the study demonstrates that while AI tools can highly effective in detecting early signs of cancer in chest X-rays, further testing is still needed before widespread implementation.